The biggest risk in the hospital is the nosocomial infection. The nosocomial infection refers to the infection acquired by the inpatient in the hospital, including the infection that occurred during the hospitalization and the infection that acquired in the hospital but occurred after discharge, which does not include the infection before admission and the infections that are already in the incubation period when admitted to the hospital. Infections acquired by hospital staff in the hospital are also nosocomial infections. Broadly speaking, the objects of nosocomial infection include inpatients, hospital staff, outpatients and emergency patients, visitors, and patient family members. These people who acquire infectious diseases in the hospital area can be called nosocomial infections, but because the outpatients , the visitor and the patient’s family members spend a short time in the hospital, and there are many and complicated factors for acquiring the infection. It is difficult to determine whether the infection comes from the hospital. Therefore, in fact, the objects of hospital infection are mainly inpatients and hospital staff.
In September 2008, 8 newborns died in an infection incident in the Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University. The Ministry of Health investigated the hospital’s ineffective implementation of the "Nosocomial Infection Management Measures" and related hospital management regulations, lax hospital management, and flaws in medical security; Ignore hospital infection management and fail to fulfill the responsibility of infection prevention and control; lack of hospital infection monitoring and conceal hospital infection events; weak infection prevention and control work; incomplete cleaning and disinfection of medical staff; the hands of medical staff, the surface of the ward, and milk bottles and nipples newborns used, and the water injection port of the newborn incubator were all tested, and it was found that the bacteria were seriously exceeding the standard, and there was obvious contamination of Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infections in hospitals have magnified the reliability of disinfection and sanitation in hospitals. Although the state has issued WS/T 367-2012 "Technical Specifications for Disinfection in Medical Institutions" and GB 15982-2012 "Hospital Disinfection and Hygiene Standards", hospitals are required to clean the environment and surfaces before disinfection; use clean cloth or disinfectant cloth to wipe the surface of cleaning treatment vehicles, diagnosis and treatment workbenches, instrument and equipment counter-tops, bedside cabinets, and newborn incubators; used cloth towels should be cleaned, disinfected and dried after each use; the floor should also be cleaned and disinfected, but the subsequent validity verification lacks clear requirements.
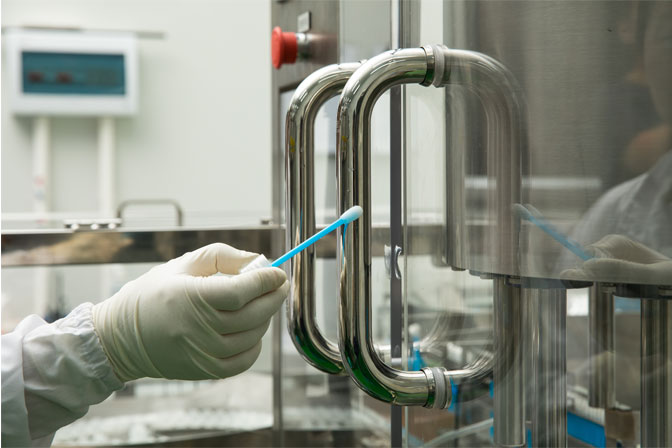

It is mentioned in the "SIFIC Best Practices for Nosocomial Infection Prevention and Control Series" that the hands of medical staff and the surface which the hands have high-frequency contact (such as bed rails, ward door handles, bedside tables, sphygmomanometers, intravenous pumps, bedside calls, light switches, toilets, etc.) should be cleaned and disinfected more frequently. Clean quality monitoring should be carried out on the surfaces that are frequently touched by hands near the patient's diagnosis and treatment area to ensure continuous and effective environmental control. Commonly used clean quality monitoring methods are visual inspection, fluorescent labeling, and microbial culture. The visual method is completely ineffective when monitoring the quality of cleanliness. The fluorescent labeling method is only aimed at the current cleaning and disinfection effect, and the microbial culture method is the most accurate indicator of potential risks.
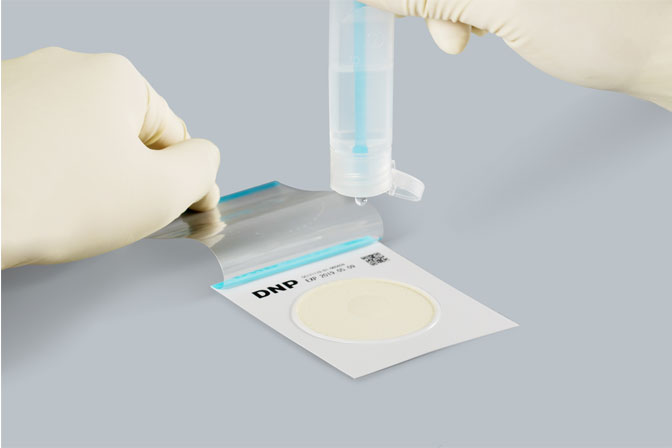
In fact, in the "SIFIC Best Practices for Nosocomial Infection Prevention and Control Series", the monitoring of high-risk places and the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) certification of food processing have the same effect. The world's first swab sampling kit to obtain HACCP certification is the ST-25 series, which is not only suitable for the sampling of microorganisms on the hands of personnel, but also for the collection of microorganisms on uneven surfaces; use contact agar medium (SAAC) for contact sampling on flat objects. Regular monitoring of the environment and personnel can effectively reflect the effects of cleaning and disinfection. Good cleaning and disinfection effects have a very important positive impact on reducing nosocomial infections.